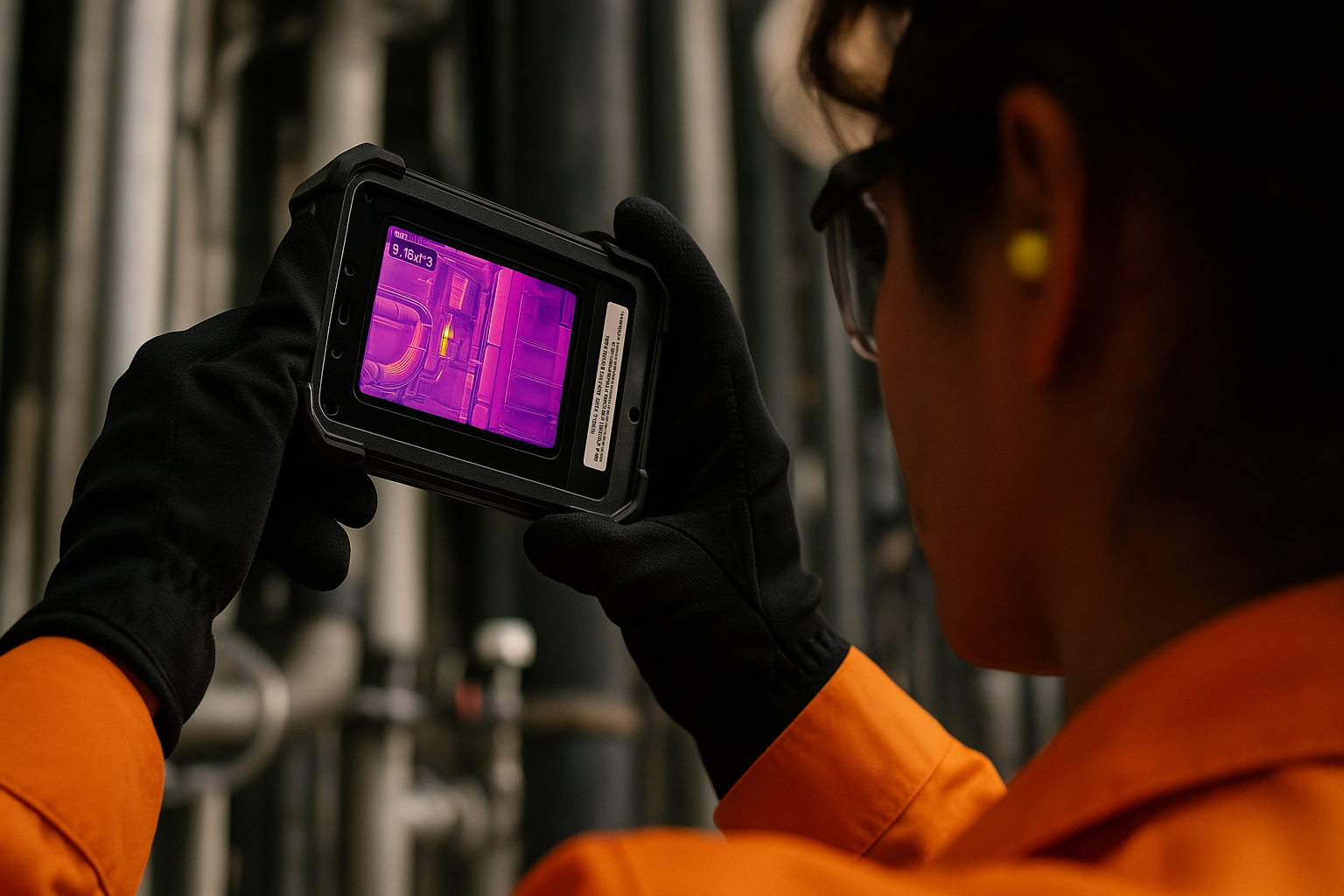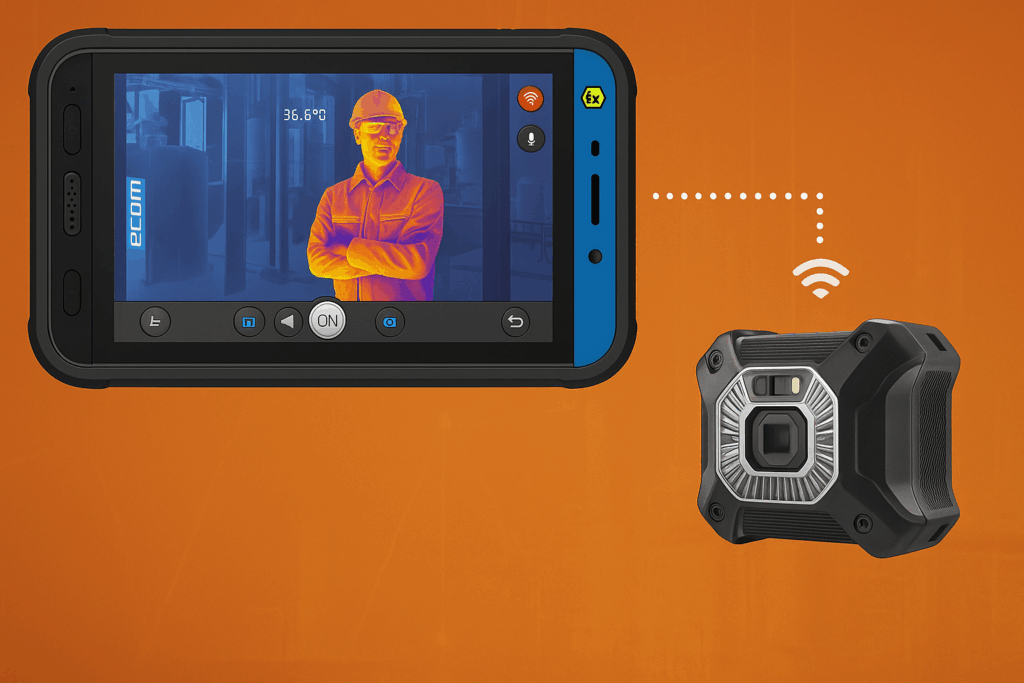
Industrial safety is evolving rapidly, with cutting-edge technologies playing an increasingly pivotal role in ensuring safe, efficient operations. One of the most transformative innovations in recent years is the integration of thermal imaging into intrinsically safe camera systems. These devices are specifically engineered for hazardous locations, combining high-resolution thermal detection with explosion-proof certifications to make inspections safer and more efficient.
Used across sectors like oil and gas, chemical manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and mining, intrinsically safe cameras with thermal imaging are not just another tool—they are an essential component of a proactive safety strategy. In this article, we’ll explore what makes these devices unique, the benefits they offer, and what to consider when selecting a thermal camera that’s intrinsically safe.
What Is an Intrinsically Safe Camera with Thermal Imaging?
An intrinsically safe camera with thermal imaging is a specialized device built to function safely in environments where explosive gases, vapors, or dust are present. Intrinsic safety means the device is designed to prevent ignition by limiting the energy (both electrical and thermal) it can emit. By incorporating thermal imaging capabilities, these cameras allow users to “see” heat signatures in real time.
This combination of safety and insight enables workers to detect potential equipment failures, energy loss, or environmental changes without physical contact. It’s especially beneficial for preventive maintenance, emergency response, and remote inspections.

Why Thermal Imaging in Hazardous Areas?
Hazardous industrial environments are typically classified into zones or divisions based on the frequency and duration of explosive atmospheres. Performing inspections in these zones using standard equipment introduces unacceptable risks. Thermal imaging offers a non-contact method to:
Detect overheating components before failure
Locate gas or liquid leaks based on temperature anomalies
Validate electrical systems are functioning within normal temperature ranges
Reduce time spent in high-risk zones by identifying issues remotely
When paired with intrinsic safety design, thermal cameras become invaluable for proactive maintenance and real-time diagnostics, all while protecting personnel from potential ignition sources.
Key Certifications to Look For
Not all cameras are safe for use in hazardous areas. Look for the following certifications to ensure compliance and safety:
ATEX (Atmosphères Explosibles): Required for devices used in explosive environments within the European Union.
IECEx (International Electrotechnical Commission System for Certification): International standard for electronic equipment in explosive atmospheres.
UL Class I Division 1: Common in North America, certifying a device is safe in areas where explosive gases are present during normal operations.
CSA (Canadian Standards Association): Required in Canada for intrinsic safety in specific industrial classifications.
Each certification indicates a level of compliance with stringent testing procedures to prevent ignition under specific conditions.
Advantages of Intrinsically Safe Cameras with Thermal Imaging
Thermal cameras with intrinsic safety certifications offer unique advantages:
1. Enhanced Worker Safety
Workers no longer need to be physically close to hot surfaces or dangerous machinery. With non-contact detection, temperature anomalies can be identified from a distance, reducing the likelihood of accidents.
2. Reduced Downtime
Early detection of issues such as overheating, friction, or fluid leaks allows operators to schedule maintenance before a critical failure occurs. This minimizes unplanned shutdowns and reduces overall repair costs.
3. Regulatory Compliance
Using certified intrinsically safe equipment helps facilities comply with national and international safety regulations, preventing costly violations and potential shutdowns.
4. Real-Time Monitoring
Many modern systems offer real-time alerts and integrations with control systems, allowing for continuous thermal monitoring in dynamic environments.
Featured Product: Dahua Complete Human Temperature Thermal System
One standout solution is the Dahua Complete Human Temperature Thermal System, designed for real-time temperature monitoring and thermal screening. While initially developed for elevated skin temperature screening during health crises, its capabilities also make it valuable in industrial settings.
Key Features
Thermal Accuracy of ±0.3°C with blackbody calibration, offering precise detection for both safety and preventive maintenance.
Non-Contact Multi-Person Detection, ideal for quickly screening groups entering a controlled area.
Real-Time Alerts for abnormal temperature readings, enabling immediate response.
Plug-and-Play Design suitable for rapid deployment in facilities with limited installation time.
This system serves as both a health screening tool and a thermal imaging solution that fits into broader plant safety strategies. When installed in process zones, entrances, or control rooms, it provides an extra layer of risk mitigation.
Technical Comparison: Dahua vs. Other Thermal Cameras
| Feature | Dahua Human Temp System | FLIR Cx5 Thermal Camera | CorDEX TC7000 Thermal Camera |
|---|---|---|---|
| Certification | ATEX, IECEx | ATEX Zone 2 | ATEX, IECEx |
| Thermal Resolution | 400 × 300 | 160 × 120 | High resolution sensor |
| Accuracy | ±0.3°C | ±2°C | ±2°C |
| Max Detection Distance | Up to 3 meters | 1.5 meters | 1 meter |
| Multi-Person Screening | Yes | No | No |
| Alert System | Real-time notifications | Audible + visual | Visual only |
| Application Use | Industrial, Public Safety | Industrial | Industrial |
| Deployment Time | Fast | Moderate | Requires setup |
Applications Across Industries
Oil & Gas
Monitor pipelines and pressure vessels without introducing ignition risks. Thermal imaging can reveal temperature differentials caused by leaks or material degradation.
Chemical Processing
Scan for overheating pumps, valves, and motors. Rapid identification of abnormal heat signatures can prevent catastrophic equipment failures.
Mining
Use in underground environments where ventilation is limited and explosive gases are common. A thermal camera can quickly identify malfunctioning electrical gear.
Food & Beverage Manufacturing
Ensure sterilization systems are operating at the required temperatures and detect thermal loss in refrigerated areas, all while complying with safety codes.
FAQs: Intrinsically Safe Thermal Imaging
How does a thermal imaging camera work?
Thermal imaging cameras detect infrared energy (heat) and convert it into a visible image. This allows operators to “see” variations in surface temperatures, even in total darkness or behind certain obstructions.
Can thermal cameras detect gas leaks?
Some thermal cameras, especially higher-end models with optical gas imaging, can visualize certain types of gas leaks based on their infrared absorption. Most entry-level models detect leaks indirectly through temperature anomalies.
What does it mean when a camera is “intrinsically safe”?
A camera is intrinsically safe when it is engineered to prevent sparks or hot surfaces that could ignite an explosive atmosphere. This is achieved through design limitations on current and voltage and robust external enclosures.
Are intrinsically safe cameras waterproof and dustproof?
Many are designed to withstand harsh environments and carry ratings such as IP65 or IP67, indicating protection against dust and low-pressure water jets or submersion.
Do thermal cameras require calibration?
Yes. For optimal accuracy, especially in applications where precise temperature measurements are critical, periodic calibration against a known reference (like a blackbody source) is necessary.
Choosing the Right Intrinsically Safe Thermal Camera
When selecting the right camera for your operation, consider the following:
Hazard Classification of Your Environment: Match the camera’s certification with your facility’s zone rating.
Required Thermal Sensitivity: Ensure the resolution and accuracy match the task—e.g., detecting small thermal variances requires higher sensitivity.
Integration Capabilities: Check if the camera can integrate with your SCADA or maintenance software.
Portability vs. Fixed Mounting: Determine if handheld or mounted cameras better suit your inspection needs.
Each of these factors will influence not only the safety of your facility but also the operational insights you can gather from thermal imaging.
Conclusion
Thermal imaging is no longer a niche feature—it’s becoming an industrial standard, especially in hazardous environments where predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring are key. An intrinsically safe camera with thermal imaging bridges the gap between safety and smart diagnostics, offering protection for both assets and workers.
Devices like the Dahua Complete Human Temperature Thermal System provide a reliable and compliant solution for real-time temperature monitoring, applicable across multiple industries. With increasing regulatory pressure and a growing focus on risk prevention, now is the time to invest in high-performance, intrinsically safe thermal imaging solutions.



























