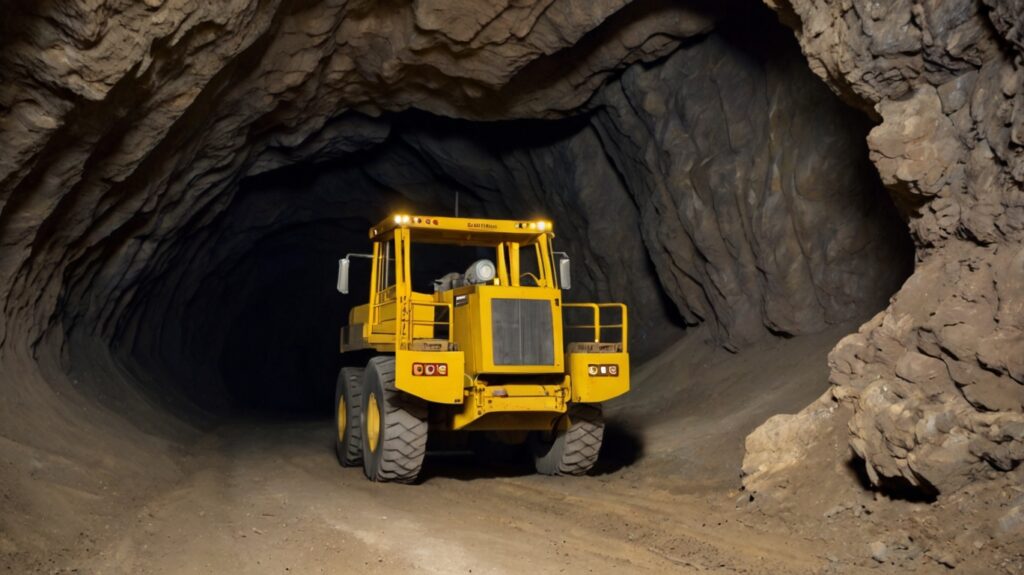
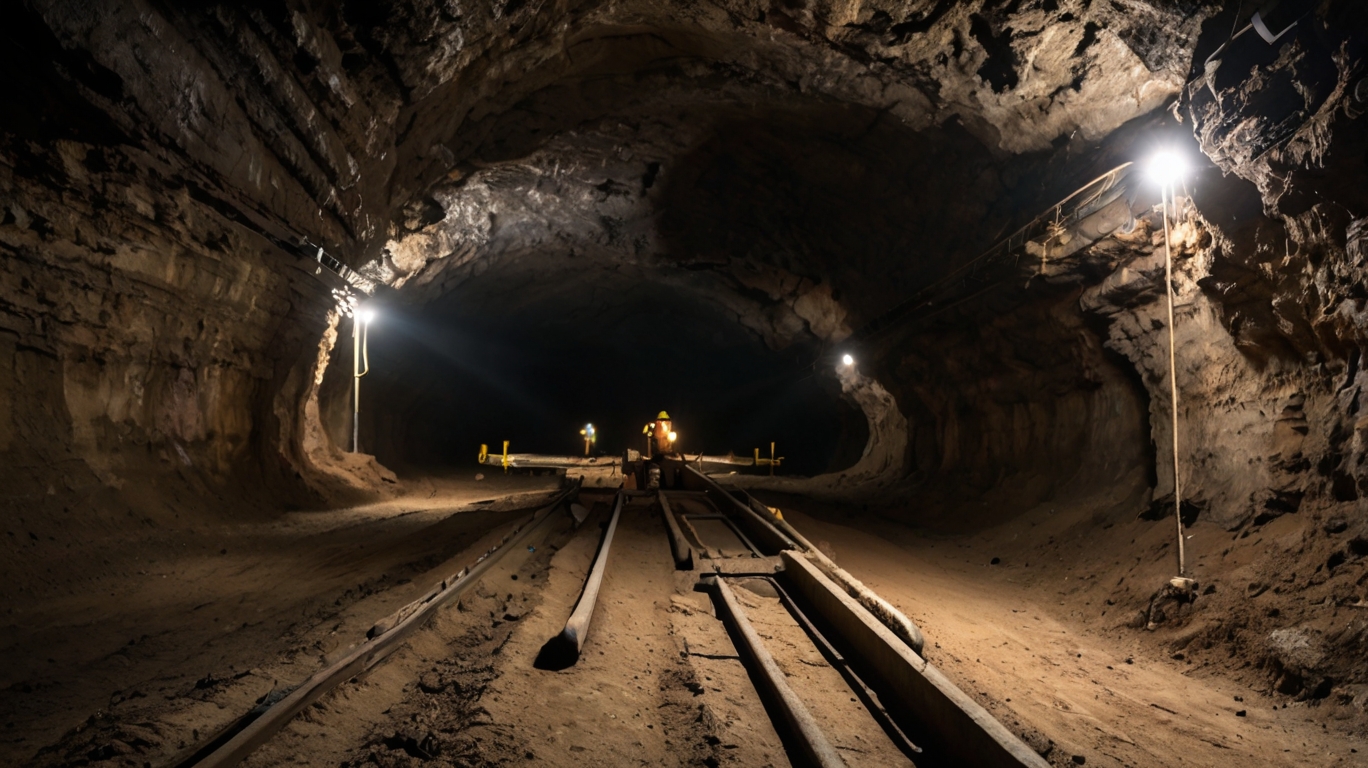
Definition: Underground mining is a method of extracting minerals, ores, and other geological materials from beneath the Earth’s surface. This process involves digging tunnels, shafts, and rooms to access the desired resources, which are then extracted using various mining techniques.
Process:
- The initial step in underground mining is development mining, where shafts and tunnels are created to access the mineral deposits.
- Different methods are employed, including room and pillar mining, narrow vein stoping, and large-scale mechanized mining. Room and pillar mining involves extracting minerals in a series of small rooms while leaving pillars of rock to support the roof. Narrow vein stoping is used for thin deposits, and large-scale mechanized mining uses advanced machinery for efficient extraction.
Support and Safety:
- To ensure the stability of the mine, various support systems are used, such as timber, steel arches, and concrete to support the mine roof and prevent collapses.
Examples in Action:
- Coal, iron ore, gold, and other precious minerals are commonly extracted through underground mining.
- Companies like Anglo American utilize advanced technologies and methods to optimize the underground mining process, ensuring safety and efficiency.
Fun Fact: Underground mining can be more environmentally friendly than surface mining because it minimizes the disruption of the surface landscape and reduces the amount of waste rock generated. However, it poses unique challenges and risks, such as ventilation issues and the potential for accidents.
- Underground mining involves the extraction of minerals deep beneath the Earth’s surface using various sophisticated methods, each tailored for specific ore body characteristics and operational requirements.
- Safety in underground mining is paramount, with advancements in intrinsically safe technology enhancing the effectiveness of traditional safety measures, reducing risks associated with volatile environments.
- Automation and cutting-edge innovations are transforming underground mining operations, enabling remote operations and improving safety and productivity while addressing inherent environmental and health hazards.
Exploring Underground Mining
Underground mining is a sophisticated process that entails extracting valuable minerals and ores buried deep below the Earth’s surface. This method is utilized when the target minerals are too deep to be mined efficiently by open-pit operations. Unlike surface mining, where the overlying rock and soil are removed, underground mining requires digging shafts, constructing tunnels, and deploying specialized equipment to reach the deposits. The process is intricate, demanding a high level of engineering prowess, safety measures, and environmental considerations.
The Role of Safety in Underground Mining
Given the inherently perilous nature of underground mining, safety remains paramount. Environments below the Earth’s surface can be volatile, with risks including gas explosions, water ingress, rock falls, and confined spaces. This is where companies like the Intrinsically Safe Store play a crucial role. Our range of certified safe products is designed to mitigate these risks, ensuring that operations can proceed without compromising the well-being of the workforce. From advanced communication tools that enable clear, uninterrupted contact between teams to robust lighting solutions that illuminate the darkest recesses of mining tunnels, every device we offer meets stringent international safety standards.
Technological Innovations Enhancing Safety
In addition to traditional safety measures, the advent of cutting-edge technology has transformed underground mining operations. Real-time monitoring systems, for instance, can now detect hazardous gas levels or structural weaknesses early, allowing for prompt corrective action. Such innovations not only bolster safety but also significantly enhance operational efficiency and productivity. The Intrinsically Safe Store is at the forefront of integrating these technological advancements into the mining sector, providing devices that support seamless operations even in the most challenging conditions.
Addressing Environmental and Health Concerns
The impact of underground mining on the environment and the health of workers is a subject of growing importance. The industry continually seeks methods to reduce its footprint and ensure that mining practices are sustainable and humane. Ventilation systems, dust control measures, and water management practices are all essential aspects of modern underground mining operations, reflecting a holistic approach to addressing the environmental and health concerns associated with this field.
Understanding the complexities and challenges of underground mining underscores the importance of adopting certified intrinsically safe devices. These tools are not merely instruments of convenience; they are vital components of a comprehensive strategy to safeguard lives, protect the environment, and maintain operational integrity in the depths below. At the Intrinsically Safe Store, we are dedicated to equipping professionals and companies operating in hazardous environments with the tools they need to navigate these challenges successfully. Our commitment to safety, efficiency, and effectiveness is unwavering, and we continue to support industries worldwide in achieving their objectives while upholding the highest standards of safety and sustainability.
Elevate Safety and Efficiency in Your Underground Mining Operations
At the Intrinsically Safe Store, we are dedicated to enhancing the safety and productivity of professionals working in hazardous environments, including the demanding and intricate world of underground mining. With our unparalleled selection of certified safe products, we stand ready to serve those who delve into the earth’s depths, ensuring that you and your team can focus on the task at hand with peace of mind.
- Explore Our Advanced Intrinsically Safe Devices: Our comprehensive catalog is designed to meet the unique challenges of underground mining. From cutting-edge communication tools that withstand the rigors of subterranean connectivity to robust lighting solutions that illuminate the darkest reaches, and vigilant monitoring systems that keep constant watch over environmental hazards, we’ve got you covered.
- Seek Expert Advice: Not sure which solutions best fit your operation? Our team of experts is here to help. With in-depth industry knowledge and a commitment to your safety, we’ll guide you through our product range, ensuring you select the devices that align with your specific needs.
- Enhance Your Operational Safety Now: Don’t wait for an incident to remind you of the importance of safety in underground mining. Reach out to the Intrinsically Safe Store today, and leverage our proven solutions to protect your most valuable asset—your people.
By choosing the Intrinsically Safe Store, you’re not just purchasing equipment; you’re investing in a safer, more efficient future for your mining operations.
Underground Mining Methods
Underground mining, a critical component of the global mining industry, employs various techniques to extract minerals and other valuable resources from beneath the earth’s surface. This section delves into the primary methods employed in underground mining, each distinguished by its unique approach to accessing and retrieving subterranean materials.
Room and Pillar Mining
Room and pillar mining is among the oldest mining methods, primarily used for flat or gently dipping ore bodies. This method involves excavating rooms within the ore body, separated by pillars of unmined material left intact to support the overhead structures. The rooms are progressively cut into the ore body while maintaining the pillars’ stability, thus allowing for the safe extraction of materials. This technique is widely favored for its efficiency and safety, especially in coal, salt, and potash mining operations.
Longwall Mining
Longwall mining, a more modern approach, is predominantly used in coal mining to extract coal along a long wall or face. The equipment used in longwall mining, a longwall shearer, moves along the face and mechanically shears the coal from the wall, allowing it to fall onto a conveyor for removal. This method is highly efficient, offering higher recovery rates than traditional room and pillar mining due to the complete extraction of coal from the seam.
Cut and Fill Mining
Cut and fill mining is a precise method often utilized in irregular ore bodies or those with varying grades. This selective method involves excavating the ore in horizontal slices, starting from the bottom and advancing upward, filling the voids with waste rock or tailings after each slice. This backfill provides support for the walls, reducing the risk of collapse and allowing for the safe extraction of valuable ore.
Block Caving
Block caving is an underground mining technique suitable for massive ore bodies with a uniform distribution of minerals. This method involves undercutting the ore body to cause it to break or “cave” under its own weight, facilitating its recovery from draw points located beneath the ore body. Block caving is recognized for its low operational costs and significant output, making it an attractive option for large-scale operations.
Stope and Retreat Mining
Stope and retreat mining, also known as stoping, removes the ore in vertical slices, advancing from the bottom upwards. After the ore is extracted, the resulting voids are backfilled, either with waste material or, as in the cut and fill method, with a mixture designed to support the mine’s structure. This technique is common in precious and base metal mining, where the economic value of the ore justifies the intricate extraction process.
Understanding the various underground mining methods is crucial for professionals in the mining industry, ensuring the selection of the most appropriate and efficient technique based on the specific characteristics of the ore body and the surrounding geological environment. At the Intrinsically Safe Store, we reinforce the importance of choosing the right mining method with an emphasis on safety and efficiency. Through our range of intrinsically safe products, we provide the tools and technology designed to protect lives in these hazardous underground environments. By offering solutions that enhance the effectiveness of these mining operations, we stand by our commitment to make every mining project safer, supporting our mission to connect people with certified safe solutions.
Ventilation and Safety Below the Surface
Ventilation in underground mining is more than just a matter of comfort; it is a critical aspect of workplace safety. Proper ventilation systems are essential in maintaining a safe environment for miners, as they help to control the levels of dangerous gases and ensure a supply of fresh air. This is crucial in preventing respiratory issues, reducing the risk of explosions, and providing a means of escape in case of emergency.
Intrinsically safe equipment plays a pivotal role in enhancing ventilation and safety below the surface. At the Intrinsically Safe Store, we understand the complex challenges faced by professionals in hazardous environments such as underground mining. Our range of certified safe products includes advanced ventilation monitoring systems that are designed to operate reliably in the demanding conditions found in mines. These systems are essential for detecting potentially harmful gases, such as methane, carbon monoxide, and hydrogen sulfide, which can accumulate in mine tunnels and pose significant health risks.
Moreover, our intrinsically safe devices are engineered to ensure communication lines remain open even in the most challenging conditions. Reliable communication is vital for coordinating evacuation procedures and ensuring that every miner is accounted for in case of an emergency. By integrating advanced technologies and adhering to stringent international safety standards, our products support the industry’s efforts to maintain a safe working environment underground.
The importance of investing in high-quality, intrinsically safe equipment cannot be overstated. It is not only about compliance with safety regulations but also about committing to the wellbeing of every individual who descends into the depths of the earth for their livelihood. As a company that prides itself on supplying a billion certified safe solutions to improve the world, making 19 people safer every minute, we are dedicated to partnering with mining professionals and companies. Together, we can enhance safety, efficiency, and effectiveness below the surface, ensuring that the challenging work of mining continues with the highest standards of protection and care.
Automation in Underground Mining
As the demand for minerals and resources grows, the mining industry has been on a constant quest for more efficient and safer methods of extraction. Automation in underground mining represents a significant leap towards achieving these goals. Embracing automation not only enhances productivity but also improves safety, making it a critical aspect for companies operating in hazardous environments.
Underground mining presents unique challenges, from navigating complex geologies to ensuring the safety of the workforce. The introduction of automated technologies in this sector has brought about transformative changes. Automated drilling rigs, load-haul-dump (LHD) machines, and conveyor systems are now commonplace in underground mines. These technologies not only streamline operations but also minimize the exposure of workers to hazardous conditions, aligning with the industry’s move towards creating safer working environments.
The integration of automation in underground mining also includes advanced communication and monitoring systems. These systems facilitate real-time data collection and analysis, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing unplanned downtime. The Intrinsically Safe Store is at the forefront of providing these sophisticated tools. Our range of intrinsically safe devices, designed to withstand the rigorous conditions of underground mining, include communication tools that ensure seamless interaction between automated machinery and the control center, as well as lighting and monitoring systems that enhance visibility and safety in the subterranean workspace.
Furthermore, the application of automation paves the way for remote operation capabilities, allowing for the remote control of machinery and operations from the surface. This not only reduces the risk of accidents by minimizing the number of personnel underground but also contributes to more efficient operation management.
At the Intrinsically Safe Store, we understand the complexities and hazards of underground mining. Our mission to connect people with certified safe solutions is more than just a business model; it’s a commitment to improving safety and efficiency in hazardous environments. By offering products that support the transition towards automated mining operations, we are contributing to an industry-wide transformation towards safer, more productive, and efficient practices.
Comparing Underground and Open-Pit Mining
When delving into the realm of mining operations, it’s crucial to understand the distinctions and applications of both underground and open-pit mining methods, as each plays a pivotal role in resource extraction while presenting unique challenges and safety considerations.
What is Underground Mining?
Underground mining, also known as subsurface mining, involves excavating minerals and ores from beneath the earth’s surface. This method is utilized when the mineral deposit is too deep to be mined economically through open-pit techniques. It entails the construction of tunnels or shafts into the earth to reach the underground deposits. The complexity of underground mining operations necessitates sophisticated equipment, skilled labor, and adherence to stringent safety protocols, especially in volatile environments where the risk of gas leaks or collapse is ever-present.
Comparison with Open-Pit Mining
On the other hand, open-pit mining, sometimes referred to as open-cast mining, involves removing layers of soil and rock to access the ore body near the surface. This method is efficient for extracting materials like coal, copper, iron, and other minerals found in sedimentary rocks. Open-pit mines are characterized by their vast, terraced walls, which allow for the easy transportation of extracted materials from the mine.
Safety and Efficiency: The choice between underground and open-pit mining largely depends on the depth and nature of the mineral deposit. However, safety and efficiency are paramount in both methods. Underground mining poses increased risks due to confined spaces, potential gas explosions, and roof collapses. In contrast, open-pit mining, while generally safer, has its own set of challenges, including large-scale environmental disruption and the risk of landslides.
Operational Efficiency: Open-pit mining allows for the extraction of minerals on a larger scale, potentially leading to more significant yields compared to underground mining. However, underground mining offers the ability to access deeper deposits, which might be more valuable, providing a potentially higher yield per square meter of mineral.
Environmental Impact: Underground mining generally has a smaller environmental footprint than open-pit mining, as it causes less surface disturbance. However, it can lead to subsidence (ground sinking) and affect groundwater flow, requiring careful management.
Economic Considerations: The cost factor heavily influences the choice between the two mining methods. Open-pit mining generally requires lower capital investment and operational costs. In contrast, the initial setup for underground mining is higher due to the need for significant reinforcement of mine structures, advanced ventilation systems, and stringent safety measures.
A Call for Safety
Regardless of the mining method, implementing the highest safety standards is non-negotiable. At the Intrinsically Safe Store, we recognize the inherent risks involved in both underground and open-pit mining operations. Our range of intrinsically safe products is designed to mitigate these risks, offering solutions that enhance safety without compromising operational efficiency. From communication tools that ensure clear, uninterrupted contact among underground workers to advanced monitoring systems that detect hazardous gases and potential structural weaknesses, our certified safe products are essential for maintaining a secure mining environment.
In the challenging and often hazardous world of mining, embracing technology and safety innovations is key to protecting lives, maximizing efficiency, and ensuring the sustainable extraction of the earth’s valuable resources.
Health Hazards in Subterranean Workplaces
When discussing what is underground mining, it’s crucial to address the inherent health hazards associated with subterranean environments. These workplaces, often far removed from the sunlight and fresh air of the surface, present unique challenges to the safety and health of the workforce.
Dust and Respiratory Diseases: One of the most significant issues in underground mining is the prevalence of airborne particulates, including silica dust from rock drilling, which can lead to severe respiratory diseases like silicosis, pneumoconiosis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The confined spaces and limited airflow of underground environments can exacerbate the concentration of such harmful particulates.
Hazardous Gases: Another considerable risk comes from the presence of hazardous gases. Methane, a highly explosive gas, is commonly encountered in coal mines, while other toxic gases like hydrogen sulfide, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen dioxide may also pose threats to miners. These gases can lead to asphyxiation or poisoning if not properly managed.
Noise and Vibration: The heavy machinery used in drilling, blasting, and transporting materials creates significant levels of noise and vibration, potentially leading to hearing loss, tinnitus, and hand-arm vibration syndrome over prolonged exposure.
Heat Stress: The deep earth’s naturally higher temperatures, combined with the heat generated by mining equipment, can lead to heat stress. If not properly managed, this may result in heat exhaustion or heat stroke, especially in physically demanding roles.
Given these hazards, the need for stringent safety measures and the implementation of intrinsically safe devices cannot be overstated. At the Intrinsically Safe Store, we understand the critical need to protect workers in these challenging environments. Our range of certified safe products, including personal protective equipment (PPE), gas detection devices, and communication tools, are designed to mitigate these health risks. Equipped with the latest in safety technology, our products are built to ensure that professionals in underground mining can operate efficiently and effectively, minimizing exposure to hazardous conditions and promoting overall well-being in subterranean workplaces.
FAQs: Understanding the Essentials of Underground Mining
What minerals are commonly extracted through underground mining?
Underground mining is utilized to extract a variety of valuable minerals from beneath the earth’s surface. This includes, but is not limited to, coal, gold, silver, uranium, copper, zinc, and lead. The method of mining selected often depends on the mineral being extracted, its location, depth, and the surrounding geology.
What is room and pillar mining?
Room and pillar mining is one of the oldest and most widespread methods used in underground mining. This technique involves creating a series of rooms or open spaces, leaving behind pillars of rock or mineral to support the roof of the mine. It is often employed in extracting coal, salt, and other easily frangible materials. Once the resource is extracted, the pillars can be removed in a controlled fashion, a process known as retreat mining.
What is longwall mining?
Longwall mining is a highly productive underground mining technique utilized primarily for the extraction of coal. In this method, a long wall of the coal seam is mined in a single slice, typically ranging from 0.6 to 1.0 meters thick. A mechanized shearer moves back and forth across the face of the seam, while hydraulic shields support the roof near the working area. Upon removing the coal, the roof is allowed to collapse in a controlled manner behind the shields, moving towards the newly extracted face.
How is ventilation managed in underground mines?
Proper ventilation in underground mines is crucial to ensure the safety and health of the workers, as it helps to control atmospheric contaminants and maintain a supply of fresh air. Ventilation is managed through a complex system of shafts, drifts, and cross-cuts that provide fresh air and circulate it throughout the mine. This system also helps to control temperature and reduce the risk of explosions by diluting and removing dangerous gases produced during the mining process.
What equipment is typically used in underground mining?
The equipment used in underground mining varies depending on the mining method, the type of mineral being extracted, and the geology of the mining area. Common equipment includes drilling machines, loaders, and trucks for material transport. Other vital equipment includes rock support and reinforcement systems, ventilation systems to ensure air quality, and various safety gear designed to protect miners in hazardous environments. Intrinsically safe devices, such as communication tools, lighting, and monitoring systems, play a crucial role in maintaining safety standards in these challenging conditions.
At the Intrinsically Safe Store, we understand the complexities and dangers of underground mining. Our range of certified safe products ensures that miners and engineers have access to the highest quality tools and equipment, designed to maximize safety and efficiency in these hazardous environments. By equipping your team with our intrinsically safe devices, you’re taking a significant step toward safeguarding their health and enhancing operational effectiveness.