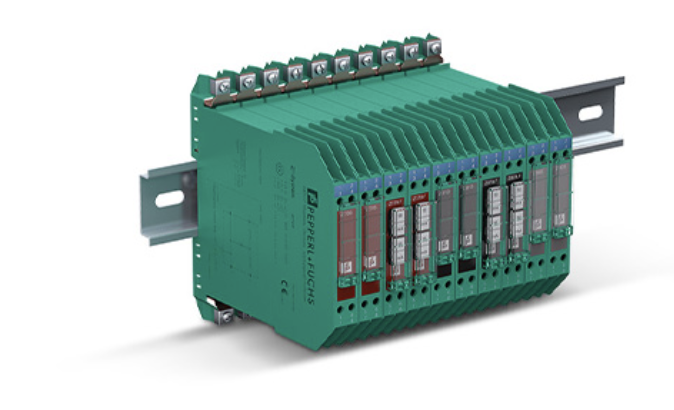
Definition: An intrinsically safe barrier is a device designed to prevent electrical energy from igniting flammable gases or vapors in hazardous environments. It limits the voltage and current to levels that are not sufficient to cause an explosion, ensuring safe operation of electrical equipment in potentially explosive atmospheres.
Science Behind It: These barriers typically use components such as Zener diodes, series current-limiting resistors, and protection fuses to divert excessive voltage or current surges safely to the system earth or ground. The primary function is to maintain the intrinsic safety of the circuit by preventing the buildup of hazardous energy levels.
Types and Installation:
- Zener Barriers: These are loop-powered, flexible, and offer high accuracy but require a low impedance ground connection. They are simpler and less expensive but may create a large voltage drop in the loop.
- Transformer Isolated Barriers (TIBs): These provide galvanic isolation between the safe area and the hazardous area, do not require a ground connection, and are more complex but offer higher voltage to the field.
- Installation Requirements: Barriers must be installed in a dust- and moisture-free enclosure, typically in a non-hazardous area, with proper separation from non-intrinsically safe wiring. A minimum separation distance of 50 mm or a conductive metallic plate grounded is required.
Examples in Action:
- Industrial Applications: Intrinsically safe barriers are commonly used in chemical plants, oil refineries, and other hazardous environments to ensure the safe operation of sensors, transmitters, and other electrical devices.
Specific Use Cases: For instance, a 0-5V sensor can be made intrinsically safe by powering it through an intrinsically safe barrier, even if the sensor itself is not rated intrinsically safe.
- Intrinsically safe barriers limit electrical and thermal energy in hazardous areas to prevent ignition of flammable materials.
- Key components of intrinsically safe barriers include energy-limiting devices, isolators, Zener barriers, grounding systems, filtering components, and safety interfaces.
- Proper installation, regular maintenance, and ongoing training are essential to ensure intrinsically safe systems perform optimally and comply with safety standards.
Introduction to Intrinsically Safe Barriers
In environments where the risk of explosions is inherent due to the presence of flammable gases, vapors, or dust, ensuring the safety of both personnel and infrastructure is paramount. This is where intrinsically safe barriers become an indispensable part of a comprehensive safety strategy.
Intrinsically safe barriers are designed to limit the energy, electrical and thermal, supplied to a device located in a hazardous area to levels below those that could ignite a specific hazardous atmospheric mixture. This protection method is critical for industries such as oil & gas, chemical, and pharmaceuticals, where the risk of an explosive atmosphere is ever-present.
The principle behind intrinsically safe barriers is relatively straightforward, yet its implementation is a product of advanced engineering. These barriers work by restricting the current and voltage that can be delivered to a device in a hazardous area. Should a fault occur, the energy released is insufficient to ignite the flammable material present. This approach does not eliminate the presence of hazardous materials but significantly reduces the risk of an ignition event, enhancing the overall safety of the environment.
Intrinsically safe barriers come in various types and configurations, each tailored to meet specific safety requirements and standards. These can range from simple zener diode barriers to more complex isolator barriers, which provide galvanic isolation to prevent high voltages or currents from entering the hazardous area. The choice of a suitable intrinsically safe barrier depends on several factors, including the type of device being protected, the specific hazardous environment, and the regulatory standards applicable to the industry and region.
The integration of intrinsically safe barriers into a facility’s safety system requires careful planning and assessment. It involves understanding the specific hazards of the operational environment, selecting appropriate intrinsically safe devices, and ensuring that the installation complies with international safety standards. This process underscores the necessity of partnering with experts in the field of intrinsically safe solutions, such as the Intrinsically Safe Store. Our comprehensive catalog of certified safe products, combined with our expertise in hazardous environments, empowers industries to maintain the highest levels of safety and compliance.
Intrinsically safe barriers represent a crucial component in the pursuit of a safer operational environment in hazardous industries. By effectively mitigating the risk of ignition, these barriers play a pivotal role in protecting lives, infrastructure, and ensuring the continuity of operations. As we continue to advance in our understanding and implementation of intrinsically safe technologies, the promise of safer and more efficient workplaces becomes a tangible reality.

Ready to Enhance Your Safety Measures?
In hazardous environments where risk is part of the job, ensuring the safety of your team and facility is paramount. At the Intrinsically Safe Store, we understand the challenges and provide solutions that don’t just meet international safety standards—they exceed them. Our commitment to safety, efficiency, and effectiveness manifests in every product we offer, from communication tools to sophisticated monitoring systems, all designed to ensure a safe and productive workplace. Consider taking action today to bolster your safety protocols:
- Explore our extensive catalog of certified safe products, curated to address the unique challenges of industries operating in hazardous environments. Whether you’re in oil & gas, mining, or pharmaceuticals, we have the intrinsically safe solutions your operations need.
- Reach out for expert advice and discover how our products can be integrated into your safety measures, ensuring not just compliance but peace of mind. Our team is ready to guide you through selecting the most appropriate intrinsically safe barriers and other devices for your specific requirements.
- Make safety a priority by choosing Intrinsically Safe Store as your partner. Our mission to make workplaces safer and more efficient drives us to offer the highest quality products and services. Connect with us now and be part of a community that values utmost safety standards.
Don’t compromise on safety. Contact the Intrinsically Safe Store today to find the ideal intrinsically safe barrier and other solutions to protect what matters most.
Components of an Intrinsically Safe Barrier System
Intrinsically safe barriers are critical components in hazardous environments, ensuring the operational integrity of electrical systems while preventing accidents. Here, we delve into the core components that constitute an intrinsically safe barrier system, offering clarity on their function and importance.
1. Energy-Limiting Devices
At the heart of an intrinsically safe barrier system are energy-limiting devices. These devices are designed to restrict electrical energy transmitted to a hazardous area, ensuring that under normal or fault conditions, the energy levels cannot ignite flammable materials. They achieve this by controlling the voltage and current to safe levels, thus, serving as the primary line of defense against potential explosions.
2. Isolators
Isolators play a crucial role in intrinsically safe barrier systems. They electrically separate the safe area circuitry from circuits in hazardous areas. This separation ensures that high voltages or faults in the system do not reach the explosive environment. Isolators come in different forms, including galvanic isolators and optical isolators, each catering to specific requirements of signal transmission and safety.
3. Zener Barriers
Zener barriers are a type of energy-limiting device that utilizes Zener diodes to clamp the voltage at safe levels. They are connected in series with a fuse and a resistor, designed to limit the current flow and drop the excess voltage, respectively. When a fault occurs, the Zener diodes conduct, the fuse blows, and the circuit is isolated, thereby preventing dangerous energy from reaching the hazardous area.
4. Grounding Systems
Proper grounding is essential in any intrinsically safe barrier system. It serves to ensure that electrical and static discharges are safely directed away from explosive atmospheres. Grounding systems are carefully designed to minimize the risk of sparks that could ignite flammable gases, vapors, or dust, thus maintaining a safer environment.
5. Filtering Components
To further enhance safety, filtering components are integrated into intrinsically safe barrier systems. These components help in suppressing noise and preventing high-frequency signals from being transmitted into hazardous areas. Filtering is especially important in complex industrial environments where electromagnetic interference (EMI) can pose additional risks.
6. Safety Interfaces
Safety interfaces, including safety relays and controllers, are integral to monitoring and managing the overall safety of a system. They can be programmed to execute specific actions when predefined conditions are met, such as isolating parts of the system in response to a fault. These interfaces provide an additional layer of control, ensuring that systems remain within safe operational parameters.
Understanding each component of an intrinsically safe barrier system is vital for professionals and companies operating in hazardous environments. Each component works in harmony to prevent ignition risks posed by electrical equipment, thereby protecting lives and assets. At the Intrinsically Safe Store, our expertise in providing certified safe products allows industries to operate efficiently and effectively, ensuring the highest levels of safety in challenging environments.
Working Principle of Intrinsically Safe Barriers
Intrinsically safe barriers are critical in preventing explosions and fires in hazardous environments by strictly controlling the electrical energy delivered to an intrinsically safe circuit. Understanding their working principle is key to appreciating their role in maintaining safety and operational integrity in high-risk industries.
At its core, an intrinsically safe barrier works by limiting the amount of energy allowed to pass into a hazardous area, ensuring that any electrical equipment operated within these areas cannot ignite an explosive atmosphere. This is achieved through two principal mechanisms: voltage limitation and current limitation.
Voltage Limitation
Voltage limitation is the process of restricting the voltage that can be supplied to a circuit to a safe level that cannot ignite a hazardous atmosphere. Intrinsic safety barriers achieve this by incorporating Zener diodes, which allow current to flow freely up to a certain threshold voltage. Beyond this voltage, the diode clamps the voltage, preventing any excess from endangering the area.
Current Limitation
Current limitation works alongside voltage limitation to ensure that the electrical current flowing into a hazardous zone is kept below the level that could produce enough heat or spark to cause an ignition. This is typically done using resistors or fuses built into the intrinsically safe barrier. By limiting the current, even if a fault occurs in the system, the barrier ensures that the energy is too low to be of any significant danger.
Fuse Protection and Redundancy
To add another layer of protection, intrinsically safe barriers often include fuses that open when they detect currents exceeding safe levels, completely isolating the downstream circuit. Some designs also incorporate redundancy, with multiple barriers in place to ensure that a single point of failure does not compromise the safety of the entire system.
Ensuring Compatibility and Safety
An integral aspect of the working principle of intrinsically safe barriers is ensuring that the barrier is compatible with the devices it is meant to protect. This involves calculating the total energy that can be stored in the circuit and ensuring it remains below the energy required to ignite the hazardous atmosphere. Engineers and safety professionals must carefully select and install intrinsically safe barriers to match the specific requirements of each device and environment, balancing safety with operational needs.
In conclusion, the principles behind intrinsically safe barriers—voltage limitation, current limitation, fuse protection, and ensuring compatibility—are fundamental to their role in protecting hazardous environments. By precisely controlling the energy that can enter such areas, these barriers play an indispensable part in preventing accidents and safeguarding lives and assets in industries faced with explosive risks.
Advantages of Using Intrinsically Safe Barriers
Intrinsically safe barriers are essential components in the toolkit of safety measures for industries operating in hazardous environments. These barriers ensure that any electrical equipment installed in these high-risk areas does not become a source of ignition. Using intrinsically safe barriers brings several key advantages that not only enhance safety but also contribute to operational efficiency and effectiveness.
Enhanced Safety
The primary advantage of using intrinsically safe barriers is the significant enhancement of safety they provide. By limiting the energy, both electrical and thermal, that can reach a potentially explosive atmosphere, these barriers substantially reduce the risk of igniting flammable gases, vapors, or dust. This intrinsic safety technology helps prevent accidents before they happen, safeguarding both personnel and assets.
Compliance with International Safety Standards
Intrinsically safe barriers are designed to meet rigorous international safety standards. Their deployment in hazardous areas helps companies comply with legal and regulatory requirements, ensuring that operations are up to global safety benchmarks. This compliance is not just about adhering to the law; it’s about embodying a commitment to the highest safety standards, underlining a company’s dedication to protecting its workforce and the environment.
Operational Continuity
One of the advantages often overlooked is the contribution of intrinsically safe barriers to operational continuity. Equipment failures or accidents in hazardous areas can lead to costly downtimes and potentially damage a company’s reputation. By employing intrinsically safe barriers, businesses can mitigate these risks, ensuring that their operations run smoothly and without interruption. This reliability is invaluable in industries where uptime is critical to success.
Cost Effectiveness
While the upfront cost of implementing intrinsically safe barriers may be a consideration, the long-term savings on insurance, compliance, and incident mitigation can be substantial. Moreover, the cost of an incident, both in human and financial terms, far outweighs the investment in intrinsically safe equipment. Thus, the use of intrinsically safe barriers is both a financially prudent and ethically responsible choice.
Ease of Maintenance
Intrinsically safe barriers and the systems they protect are generally easier and safer to maintain. Since the equipment operates at energy levels that are not capable of causing ignition, maintenance work can often be performed without shutting down operations, making it less disruptive and more cost-effective. This ease of maintenance supports a more efficient operational workflow, contributing to overall productivity.
Versatility and Scalability
Finally, intrinsically safe barriers are versatile and scalable. They can be used in a variety of hazardous environments and can be adapted to protect an ever-growing range of equipment and systems. As a company’s operational needs evolve, these barriers can be scaled and expanded to accommodate new technologies or increased capacities.
In conclusion, the advantages of using intrinsically safe barriers in hazardous environments are compelling. They represent a critical investment in safety, compliance, and operational efficiency. At the Intrinsically Safe Store, we understand the importance of these benefits. Our expertise and wide range of certified safe products are here to support your commitment to creating a safer work environment.
Installation and Maintenance Best Practices
When integrating intrinsically safe barriers into a hazardous environment, it’s crucial to adhere to established best practices to ensure optimal safety and efficiency. These guidelines not only help in maintaining the integrity of the safety barriers but also ensure they perform their intended function effectively, without compromising the safety of the environment and its occupants.
Prioritize Professional Installation
- Certified Technicians: Always rely on professionals with specialized training and certification in installing intrinsically safe barriers. Their expertise guarantees that the installation complies with international safety standards and regulations specific to your industry.
- Compliance with Standards: Ensure that the installation process adheres to relevant standards such as ATEX in Europe, or NEC 505 and NEC 500 in the United States. Compliance not only ensures safety but also legal and regulatory adherence.
Regular Inspection and Maintenance
- Scheduled Inspections: Conduct regular, scheduled inspections of intrinsically safe barriers to identify any potential wear and tear or malfunctions that could compromise safety. Recommended frequencies can vary, but a common practice is bi-annual inspections.
- Immediate Repairs: If any issues are detected during inspections, prioritize immediate repair or replacement to prevent any potential safety hazards. Use only certified parts and accessories for replacements to maintain the intrinsic safety certification.
- Document Maintenance: Keeping a detailed record of all inspections, maintenance, and repairs is crucial for internal audits and regulatory compliance. Documentation should include dates, findings, actions taken, and the personnel involved.
Enhancing Safety through Proper Training
- Educating Employees: Ensure that all personnel who interact with or are responsible for the safe barriers receive thorough training on their operation, maintenance, and emergency procedures. Well-informed employees can significantly reduce the risk of accidents.
- Updating Safety Protocols: As technology and standards evolve, so should your safety protocols. Regularly review and update safety procedures to incorporate the latest best practices and technological advancements.
Leveraging Manufacturer Support
- Utilize Technical Support: Take advantage of the support and resources offered by your intrinsically safe barrier manufacturer or supplier. They can provide valuable guidance on installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting.
- Ongoing Education: Engage with workshops, webinars, and training sessions provided by manufacturers to stay informed about the latest developments and innovations in intrinsically safe technology.
Implementing these best practices for the installation and maintenance of intrinsically safe barriers is pivotal in maintaining a safe working environment in hazardous areas. By doing so, professionals and companies not only ensure the safety of their employees and operations but also align with regulatory requirements and best practices in industry-specific hazardous area management.
Future Outlook on Intrinsically Safe Systems
As technology advances, the development and implementation of intrinsically safe systems continue to evolve, presenting new opportunities and challenges for industries operating in hazardous environments. The outlook for intrinsically safe systems is promising, with a focus on innovation, enhanced safety measures, and global standards harmonization. This progression not only signifies better protection for workers but also points towards more efficient and reliable operations across industries like oil and gas, chemical, and pharmaceuticals.
Innovation and Technological Advances
The future of intrinsically safe barriers and systems is tightly coupled with technological innovation. Advances in materials science are expected to lead to the development of new, more robust barriers that can withstand harsher conditions while ensuring safety. Likewise, digital technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT) are set to further integrate with intrinsically safe systems, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. This integration will allow for immediate detection of any barrier integrity issues or hazardous conditions, significantly reducing the risk of accidents.
Enhanced Safety Measures
As regulatory bodies and companies continue to prioritize safety, the demand for intrinsically safe systems that go beyond current standards is growing. Future developments will likely focus on creating systems that not only prevent ignition but also help in actively diagnosing potential safety threats before they become hazardous. This proactive approach to safety can significantly minimize the risk of incidents in hazardous environments, ensuring that operations are not just compliant with safety regulations but are also setting new benchmarks for industry best practices.
Global Standards Harmonization
The globalization of industries has underscored the need for harmonized safety standards across borders. The future outlook points towards a more unified set of global standards for intrinsically safe systems, facilitating easier compliance for multinational companies and promoting a higher level of safety worldwide. This harmonization is also expected to simplify the certification process for intrinsically safe devices, making it easier for companies like the Intrinsically Safe Store to offer a wider range of certified safe products to various markets.
In conclusion, intrinsically safe systems are on a path of continuous improvement, driven by technological innovation, a dedication to enhanced safety, and the movement towards global standardization. For professionals and companies operating in hazardous environments, staying abreast of these developments is crucial. At the Intrinsically Safe Store, we remain committed to leveraging these advancements to provide our customers with cutting-edge intrinsically safe solutions, ensuring that safety, efficiency, and effectiveness remain at the forefront of everything we do.
FAQs on Intrinsically Safe Barriers
Hazardous environments demand stringent safety measures to prevent accidents and ensure the safety of personnel and equipment. Intrinsically safe barriers are crucial components in achieving this level of safety. Below, we explore some frequently asked questions about intrinsically safe barriers to provide deeper insights into their importance, functionality, and implementation.
Why are intrinsically safe barriers used in hazardous environments?
Intrinsically safe barriers are used in hazardous environments to prevent the ignition of flammable gases, dust, or vapors. These barriers limit the energy (electrical and thermal) available to a circuit or device to levels insufficient to cause ignition. By doing so, they significantly reduce the risk of explosions, thereby protecting both personnel and equipment in industries like oil & gas, chemical, and pharmaceuticals.
How do intrinsically safe barriers work?
Intrinsically safe barriers work by restricting the electrical energy transmitted to a device in a hazardous area to safe levels. The barrier either absorbs or diverts excess energy, ensuring that any electrical equipment connected to it cannot produce a spark or heat sufficient to ignite the surrounding atmosphere. This is achieved through zener diodes, resistors, and fuses designed specifically for this purpose, ensuring the operational integrity of both the safety system and the device it protects.
Can intrinsically safe barriers be used with any equipment?
Intrinsically safe barriers are designed to be used with equipment that is certified as intrinsically safe (IS). Equipment must be specially designed or certified to ensure it does not store or generate energy levels capable of causing ignition. When selecting equipment for use in hazardous areas, it’s crucial to verify compatibility with IS barriers to maintain the integrity of your safety systems.
What certifications should I look for in intrinsically safe barriers?
When selecting intrinsically safe barriers, look for certifications from recognized safety organizations, such as ATEX, IECEx, FM Approvals, or CSA. These certifications indicate that the product has been rigorously tested and meets specific safety standards for use in hazardous environments. Ensure that the certification matches the specific hazardous zone classifications and requirements of your operations.
How do I install an intrinsically safe barrier?
The installation of an intrinsically safe barrier should be carried out by a qualified professional, adhering to the manufacturer’s instructions and relevant safety standards. The process typically involves connecting the barrier between the control system and the intrinsically safe device. Proper grounding, shielding, and segregation from non-IS circuits are essential to prevent energy transfer that could compromise safety. Consulting with an expert or the barrier manufacturer is highly recommended to ensure compliant and safe installation.
By incorporating intrinsically safe barriers into your safety protocols, you leverage a proven method of reducing the risk of explosions due to electrical equipment in hazardous environments. The Intrinsically Safe Store is committed to providing you with certified safe solutions and expert advice to ensure your operations are safe, efficient, and effective.