In a world where technology continues to advance rapidly, importance of industry standards cannot be overestimated. Nowhere is this more critical than in hazardous areas. Hazardous areaes have flammable gases, vapors, and combustible dust which poses significant risks to human life and property. To ensure the safety of personnel and facilities, global hazardous area safety standards have been established. In this article, we will explore the complexities of navigating these standards and provide a comprehensive global overview to help businesses and professionals effectively manage hazardous areas.
Understanding Hazardous Areas.
Before delving into safety standards, it’s essential to comprehend what hazardous areas are and why they require specific safety measures. Hazardous areas are locations where the atmosphere contains or may contain flammable gases, vapors, or combustible dust. These areas can be found in a wide range of industries, including petrochemical, manufacturing, mining, and pharmaceuticals, among others.
The explanation for hazardous areas and intrinsic safety is well explained in the video below by Thorne and Derrick.
The Role of Global Standards.
Given the global nature of many industries, it’s crucial to have harmonized safety standards that can be applied consistently across borders. These standards ensure a uniform approach to hazardous area safety. This makes it easy for multinational corporations to comply with regulations and maintain a high level of safety worldwide.
IECEx (International Electrotechnical Commission System for Certification to Standards Relating to Equipment for Use in Explosive Atmospheres).
IECEx is an internationally recognized certification system for electrical and non-electrical equipment used in explosive atmospheres. It provides a framework for manufacturers to obtain certification, ensuring that their products meet global safety requirements. IECEx certification simplifies the process of exporting and importing equipment for use in hazardous areas.
The IECEx System consists of the following components:
- The IECEx Scheme for Certified Equipment.
- The IECEx Scheme for Certified Service Facilities.
- The IECEx System for Licensing the Conformity Mark.
- The IECEx System for Certifying Personnel Competencies (CoPC).
ATEX (Atmosphères Explosibles)
ATEX is a European Union directive and certification system that applies to equipment and protective systems intended for use in potentially explosive atmospheres. While it primarily pertains to the European market, its principles and standards are widely recognized and adopted globally.
NEC (National Electrical Code) and CEC (Canadian Electrical Code).
The NEC and CEC are North American standards that provide guidelines for the installation of electrical equipment in hazardous locations. These codes are essential for ensuring the safety of installations in the United States and Canada.
The National Electrical Code® (NEC) holds the distinction of being the most universally embraced code globally. It has received approval from the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and stands as the most comprehensive compilation of regulations governing electrical installations. Its primary aim is ensuring safety for individuals and property. Familiarity with the NEC is an integral aspect of conducting operations within the electrical industry and particularly in hazardous locations.
NEC Article 504 addresses the planning, arrangement, and setup of electrical equipment and systems that do not have the potential to discharge adequate electrical or thermal energy to initiate flammable or combustible atmospheres.
ISA (International Society of Automation)
ISA standards, such as ISA-60079 series, offer valuable guidance for the design, installation, and maintenance of equipment in hazardous areas. These standards are widely accepted and used in various industries globally.
This standard focuses on categorizing areas where the potential for flammable gas, vapor, or mist-related dangers exists. It serves as a foundation for guiding the appropriate choice and setup of equipment to be used in hazardous environments.
It is meant to be implemented in situations where there is a risk of ignition caused by the presence of flammable gas or vapor when mixed with air under typical atmospheric conditions. However, it does not apply to certain situations including:
- Mines susceptible to firedramp.
- The processing ad manufacture of explosives.
- Areas where a hazard may arise due to the presence of combustible dusts or fibres (refer to IEC 61241-10 / IEC ANSI/ISA-60079-10-2);
- Catastrophic failures which are beyond the concept of abnormality dealth with in this standard.
- Rooms used for medical purposes.
- Domestic premises.
Regional Variations in Hazardous Area Classifications
While global standards such as IECEx and ATEX provide a foundation for hazardous area safety and explosion-prone locations, it is imperative to recognize that regional variations and regulations have an influence. Regional regulations play a crucial role on how the standards are implemented. Hazardous area classification is one area where such variations are prominent.
1. North America (NEC and CEC)
In North America, hazardous areas are classified into divisions and zones. The NEC (National Electrical Code) and CEC (Canadian Electrical Code) are widely used to define these classifications:
- Class I pertains to areas with flammable gases, vapors, or liquids.
- Class II applies to areas with combustible dust.
- Class III relates to areas with easily ignitable fibers or flyings.
Each class is further divided into divisions (Division 1 and Division 2) and zones (Zone 0, Zone 1, and Zone 2), depending on the level of risk and the likelihood of the hazardous substance’s presence.
2. Europe (ATEX)
In Europe, hazardous areas are classified into zones, with ATEX directives providing the framework. These zones are defined as follows:
- Zone 0 represents areas where explosive atmospheres are continuously present or present for long periods.
- Zone 1 covers areas where explosive atmospheres are likely to occur in normal operation.
- Zone 2 includes areas where explosive atmospheres are not likely to occur but may do so occasionally.
The key difference here is the emphasis on zones rather than divisions, reflecting a different approach to managing hazardous areas.
3. Australia and New Zealand
Australia and New Zealand follow their own hazardous area classification system, known as the IECEx CoPC (Certificate of Personal Competency) system. This system classifies hazardous areas into zones similar to the European approach.
Compliance Challenges in the Market.
Navigating the complex landscape of global hazardous area safety standards can be challenging for businesses operating in multiple regions. Here are some of the key challenges and considerations:
1. Regulatory Compliance.
Meeting regulatory requirements is non-negotiable. Failure to comply with local safety regulations can result in hefty fines, legal repercussions, and, most importantly, endangering lives. Businesses must stay informed about evolving regulations and ensure they align with global safety standards.
2. Product Certification.
Obtaining the necessary certifications, such as IECEx or ATEX, can be a complex and costly process. However, it is vital for manufacturers to ensure their products meet international safety standards to access global markets. Certification streamlines the approval process and increases the marketability of products.
3. Training and Competency.
Personnel working in hazardous areas must receive proper training and certification to ensure their competence and safety. Different regions may have distinct training requirements and certification processes. Businesses must invest in ongoing training and development to maintain a skilled and compliant workforce.
4. Documentation and Record Keeping.
Maintaining accurate records of equipment, inspections, and compliance activities is essential. This documentation helps demonstrate compliance with safety standards and simplifies regulatory audits.
Best Practices for Navigating Global Hazardous Area Safety Standards.
To successfully navigate the complexities of global hazardous area safety standards, businesses and professionals should consider the following best practices:
- Conduct a Hazardous Area Assessment
Before implementing safety measures, conduct a thorough assessment of the hazardous area to determine its classification and the potential risks involved. This assessment serves as the foundation for compliance efforts.
- Engage Local Experts
Leverage the expertise of local safety professionals who are well-versed in regional regulations and standards. These experts can provide invaluable guidance and ensure compliance with local requirements.
- Standardize Where Possible
Wherever feasible, standardize equipment and processes across different regions to simplify compliance efforts. This can reduce costs and streamline maintenance and training.
- Keep Abreast Regulatory Changes
Stay up-to-date with changes in regional regulations and safety standards. Regulatory bodies frequently update guidelines to reflect advances in technology and changes in industry practices.
- Invest in Training and Education
Prioritize training and education for personnel working in hazardous areas. Well-trained employees are essential for maintaining safety and compliance.
- Leverage Technology
Utilize advanced technologies, such as real-time monitoring systems and digital record-keeping tools, to enhance safety and streamline compliance efforts.
- Collaborate with Industry Associations
Join industry associations and networks that focus on hazardous area safety. These organizations often provide resources, best practices, and opportunities for knowledge exchange.
Where do you find certifications when you are purchasing a product from Intrinsically Safe Store?
Good news. All intrinsically safe products sold at our store come with certifications and you can check by following the following steps:
- In our website homepage, select the product category page where your product will be found.
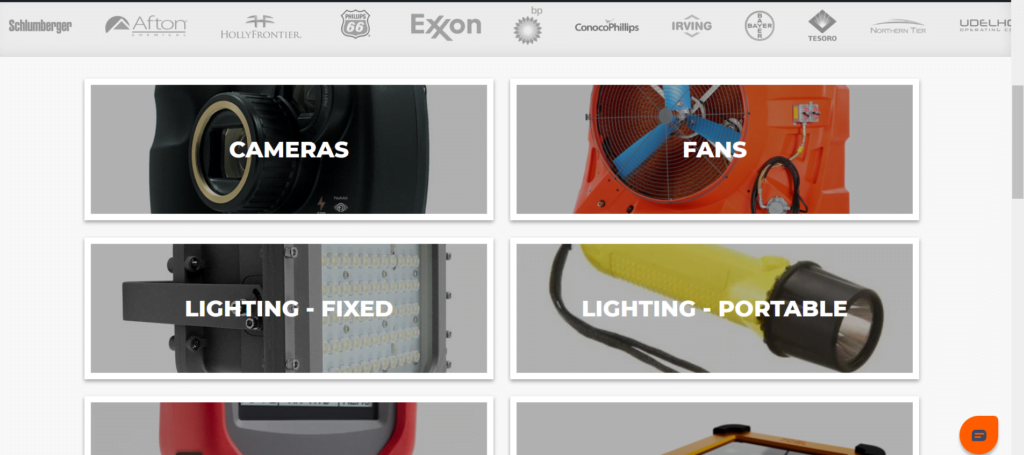
- Find and navigate to the product you are interested in and click on it.
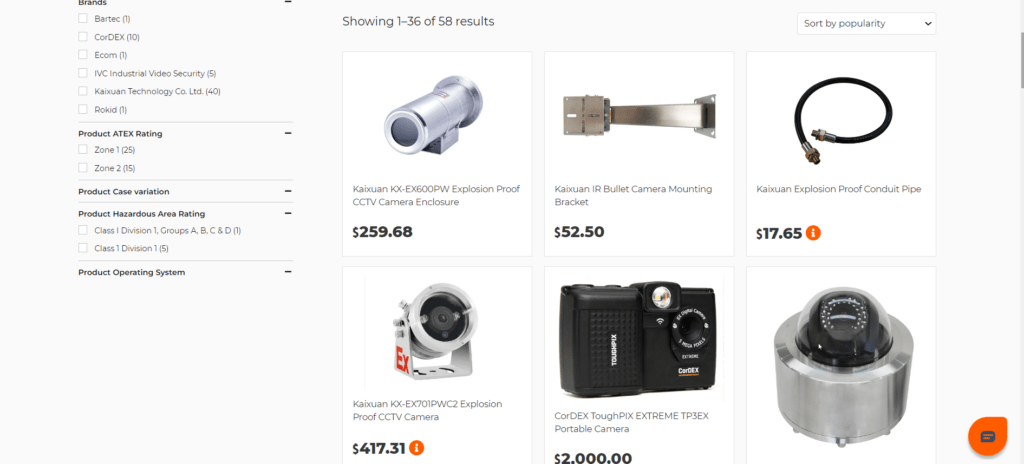
- Once you find a match for the product you are looking for, click on it to open the product page.
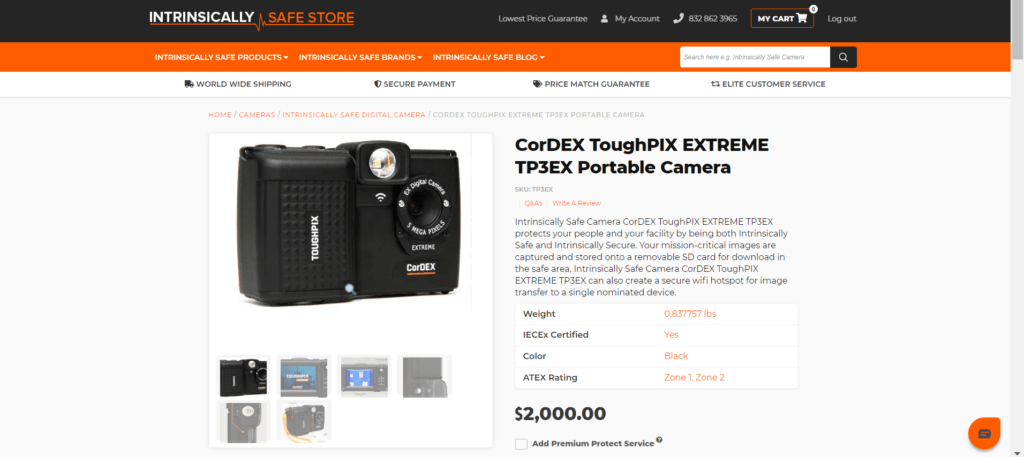
- The product description will indicate the certification type and status. Scroll down to the bottom of the product page and you will see the links to the certifications.
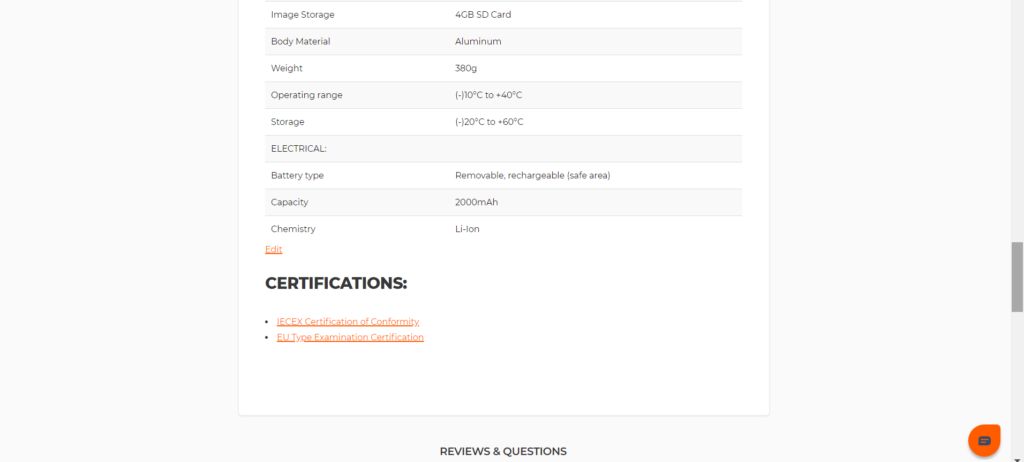
- Click on the certificate to download.
In a world where globalization has led to increased business operations across borders, navigating hazardous area safety standards is a critical challenge.
However, by understanding the key global standards, recognizing regional variations, and implementing best practices, businesses and professionals can effectively manage hazardous areas and ensure the safety of personnel and facilities.
In doing so, they not only meet compliance requirements but also demonstrate a commitment to the well-being of all those working in and around potentially explosive atmospheres.


